- +994 55 217 57 77
- info@aytenbabaxanova.az
- Melhem International Hospital

Goiter disease is a condition characterized by the dysfunction or enlargement of the thyroid gland. This condition can occur not only in adults but also in children and adolescents. Improper functioning of the thyroid gland can disrupt the body's hormonal balance and significantly affect the physical and psychological development of children. In this article, we will discuss how goiter disease is treated in children and adolescents and which symptoms should be carefully monitored.
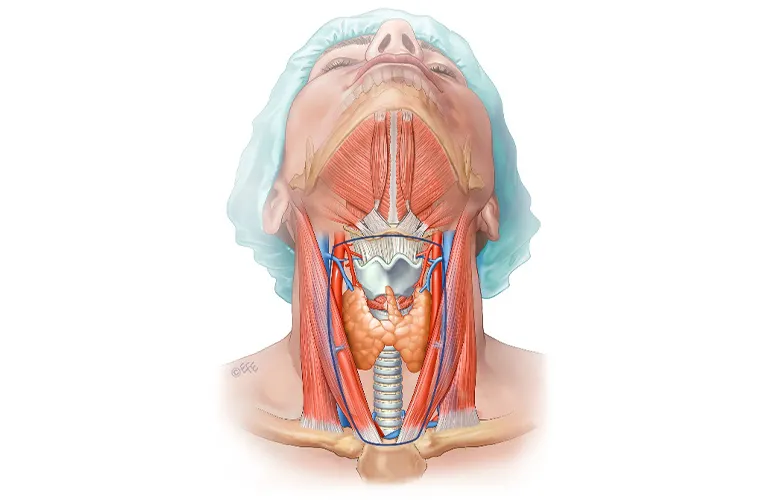
Goiter is a disease characterized by the enlargement of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland, located in the neck region, produces hormones (T3 and T4) that regulate the body's metabolism. Any disruption in the levels of thyroid hormones can negatively affect various bodily functions. Goiter disease in children and adolescents may occur due to both genetic and environmental factors.
The symptoms of goiter disease in children and adolescents may be less obvious compared to adults. The following signs may indicate goiter in children:
The treatment of goiter disease in children varies depending on the type of the condition and the child's age. Treatment methods include medication therapy, surgical intervention, and nutritional adjustments.
Iodine is essential for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland. Iodine deficiency is one of the primary causes of goiter disease. Therefore, iodine-rich foods such as seafood and iodized salt should be included in the child’s diet. In some cases, doctors may prescribe additional iodine supplements.
Medication is the most common treatment option for goiter disease in children. Medication therapy varies depending on the type of the disorder:
In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to treat goiter. If the thyroid gland becomes significantly enlarged or if other medical complications occur, partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary. Surgery is generally recommended in severe cases.
Special attention must be given during the treatment of goiter disease in children and adolescents. Early diagnosis and timely treatment can prevent more serious health complications in the future.
 Zob Xəstəliyinin Qidalanmaya Təsiri
Zob Xəstəliyinin Qidalanmaya Təsiri
 Thyroid gland
Thyroid gland
 Short stature in children
Short stature in children
 Diabetes Type I - Known Misconceptions
Diabetes Type I - Known Misconceptions
Copyright @ 2023 Aytenbabaxanova.az.