- +994 55 217 57 77
- info@aytenbabaxanova.az
- Melhem International Hospital
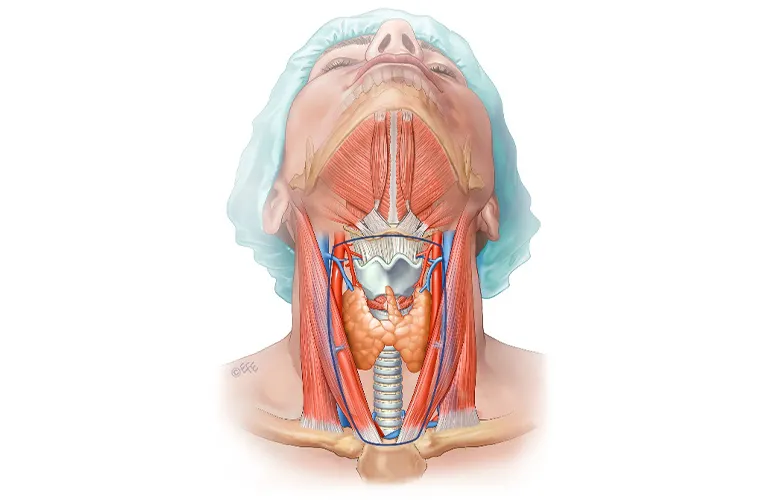
Goiter, also known as a thyroid disorder, occurs when the thyroid gland — a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the neck — fails to function properly. The thyroid regulates metabolism, energy production, and body temperature. Therefore, proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining the healthy function of the thyroid gland. This article explores how diet influences thyroid health and which foods can support its function.
The thyroid gland produces the hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), which regulate the body's metabolism, energy levels, and overall growth processes.
Disorders of the thyroid are generally classified into two main categories:
Balanced nutrition plays a key role in supporting the thyroid. While some foods enhance thyroid function, others may negatively affect it.
Iodine-Rich Foods
Iodine is an essential mineral for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency can lead to goiter and hypothyroidism, while excessive intake may also be harmful.
Recommended sources: seafood, iodized salt, milk and dairy products, eggs.
Selenium-Rich Foods
Selenium helps convert thyroid hormones into their active forms and provides antioxidant protection. Adequate selenium intake supports thyroid health and hormone balance.
Recommended sources: Brazil nuts, fish, eggs, whole grains, legumes.
Vitamin C and Antioxidants
Vitamin C and other antioxidants protect thyroid cells from oxidative stress and strengthen the immune system, which indirectly supports thyroid function.
Recommended sources: citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, broccoli, red bell pepper.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and help maintain hormonal balance. They are beneficial for overall health in individuals with thyroid disorders.
Recommended sources: salmon, sardines, tuna, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D supports immune function and helps prevent thyroid-related autoimmune diseases. It can be obtained through sunlight exposure and diet.
Recommended sources: egg yolks, fatty fish, fortified dairy products.
Zinc
Zinc is an important mineral that supports the production of thyroid hormones. Its deficiency may weaken thyroid function and slow metabolism.
Recommended sources: red meat, poultry, legumes, seafood, nuts.
Certain foods can interfere with thyroid activity, especially when consumed in large quantities. It is important to be mindful of the following:
Maintaining a healthy diet is essential for managing goiter and other thyroid-related disorders. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet helps stabilize thyroid function, supports medical treatment, and promotes overall well-being.
 Goiter Disorder in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
Goiter Disorder in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
 Thyroid gland
Thyroid gland
 Short stature in children
Short stature in children
 Diabetes Type I - Known Misconceptions
Diabetes Type I - Known Misconceptions
Copyright @ 2023 Aytenbabaxanova.az.